1. The Pacesetting Leader
The pacesetting leader is a leadership style identified by Daniel Goleman in his work on emotional intelligence and leadership. It’s characterized by a leader who sets high standards and leads by example, expecting team members to follow their lead with similar excellence and speed. Here’s a closer look at what defines a pacesetting leader and some of the benefits and challenges associated with this style.

Characteristics of a Pacesetting Leader
High Performance Standards: Pacesetting leaders set ambitious goals and expect their team members to meet those standards, often without much need for supervision.
Leading by Example: They demonstrate the level of effort, quality, and pace they expect from others, creating a model for the team to emulate.
Quick Execution: This leadership style emphasizes speed and efficiency, with a preference for quick results and immediate impact.
Self-Motivated and Detail-Oriented: Pacesetting leaders are often self-driven and detail-focused, which can be motivating for team members who seek to perform at a high level.
Benefits of the Pacesetting Style
Boosts High Performance: For teams that are already skilled and highly motivated, a pacesetting leader can inspire them to push their limits and achieve peak performance.
Encourages Efficiency: By focusing on fast, high-quality output, the pacesetting leader can help teams deliver results quickly, which can be particularly useful in fast-paced industries.
Promotes Accountability: The leader’s high standards hold team members accountable for their contributions, which can foster a sense of responsibility and commitment.
Challenges of the Pacesetting Style
Potential Burnout: Because the pacesetting style demands intense focus, speed, and perfection, team members may experience stress and burnout, particularly if they feel they can’t meet the leader’s high standards.
Reduced Innovation and Morale: Constant emphasis on efficiency can stifle creativity, as team members may feel discouraged from experimenting or learning at a slower pace.
Lack of Empathy and Support: This leadership style can sometimes neglect the emotional and developmental needs of the team, as it may focus too heavily on output rather than team welfare.
When to Use Pacesetting Leadership
Pacesetting leadership works best in situations where:
The team is highly competent, motivated, and skilled.
Quick results are necessary, and the tasks are clearly defined.
Team members are self-starters and thrive with minimal guidance.
2.The Authoritative Leader
The concept of an “authoritative leader” refers to a leadership style where the leader sets a clear vision and direction, establishes guidelines, and expects adherence to standards, often with a degree of control and oversight. Unlike authoritarian leadership, which can be rigid and punitive, authoritative leadership balances control with motivation and support.
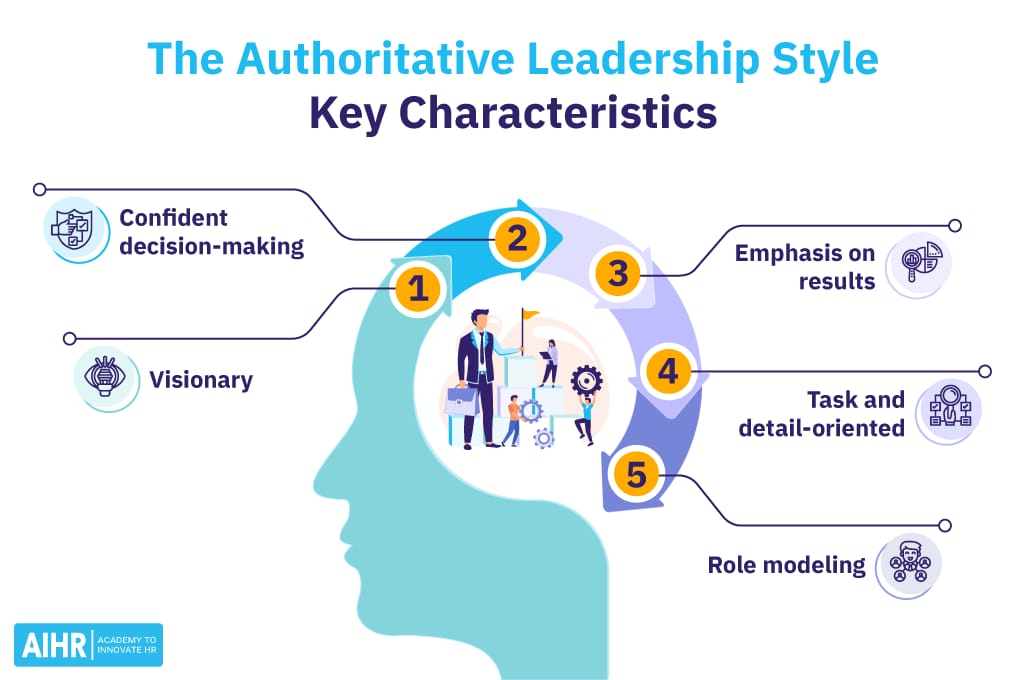
Key traits of an authoritative leader include:
Clear Vision: They articulate a compelling vision and set clear goals, providing direction and purpose to the team.
Confidence and Decisiveness: Authoritative leaders make decisions confidently, inspiring trust in their abilities and judgment.
Guidance and Support: They guide their teams by setting expectations and providing support, ensuring that members understand the objectives and feel equipped to meet them.
Inspiration and Motivation: These leaders foster loyalty and motivation by connecting individual tasks to a broader mission, emphasizing the value of each role.
Encouragement of Initiative: Authoritative leaders encourage team members to take ownership of their work, offering a balance of direction and autonomy.
3.The Affiliative Leader
An affiliative leader prioritizes people, relationships, and emotional harmony within a team. This style of leadership focuses on building a positive and inclusive work environment where team members feel valued, understood, and connected. Affiliative leaders tend to be supportive and empathetic, often putting the well-being and morale of their team above strict adherence to deadlines or rules. They frequently offer praise, encourage open communication, and foster a collaborative atmosphere.

Key Characteristics of Affiliative Leadership:
Pros of Affiliative Leadership:
Empathy and Compassion: Affiliative leaders are sensitive to their team members’ needs and feelings, making them approachable and trustworthy.
Conflict Resolution: By valuing emotional intelligence, these leaders can address and resolve conflicts effectively, reducing tension and misunderstandings.
Team Building: An affiliative leader focuses on strengthening bonds between team members, fostering unity and teamwork.
Positive Reinforcement: Rather than criticizing, they offer constructive feedback and praise to build confidence and motivation.
Supportive Environment: They prioritize work-life balance and create a safe space where employees feel comfortable sharing ideas and challenges.
Pros of Affiliative Leadership:
Boosts Team Morale: The focus on relationships and well-being improves team morale and loyalty.
Encourages Open Communication: Team members are more likely to voice their opinions and concerns.
Enhances Collaboration: By fostering trust and understanding, team members work better together.
Reduces Stress: Supportive leadership can decrease work-related stress and burnout.
Cons of Affiliative Leadership:
Can Compromise Performance: A strong focus on relationships may sometimes lead to lower productivity if not balanced.
Difficult in High-Pressure Situations: This style may be less effective when quick decision-making or a strong directive is needed.
Risk of Favoritism: Affiliative leaders might unintentionally favor certain team members, which could lead to resentment or division.
When Affiliative Leadership Works Best:
After Major Changes or Crises: When a team is feeling demoralized or disconnected, affiliative leaders can help rebuild trust.
In Creative or Collaborative Roles: Encouraging open communication is essential in roles that rely on teamwork and innovation.
For Long-Term Projects: It’s beneficial in environments where team cohesion is essential for sustained success.
4.The Coaching Leader
The role of a coaching leader is both inspirational and supportive, focusing on guiding team members to develop their skills and reach their full potential. Rather than simply managing tasks, a coaching leader invests time in nurturing individual talents and aligning personal goals with team and organizational objectives. Here are some key characteristics and practices of a coaching leader:

Active Listening
A coaching leader listens attentively to understand each team member’s challenges, aspirations, and ideas. This fosters a safe environment where team members feel valued and heard.
Guidance Over Direction
Instead of micromanaging, a coaching leader provides guidance, helping team members find their own solutions. This builds problem-solving skills and encourages a sense of ownership.
Empowering Through Questions
Coaching leaders use open-ended questions to encourage self-reflection and critical thinking. Questions like, “What do you think would be the best approach?” or “How could you solve this challenge?” help individuals become more resourceful and confident.
Focus on Development
Development of skills and knowledge is a priority. A coaching leader provides feedback that is constructive and oriented toward growth, pointing out areas for improvement while celebrating strengths and achievements.
Goal Alignment
Coaching leaders work with each team member to set personal goals that align with the team’s and organization’s vision. This ensures that each individual feels their contributions are purposeful and that their career aspirations are supported.
Providing Regular, Constructive Feedback
Feedback is given frequently rather than waiting for formal performance reviews. Coaching leaders focus on what team members did well and how they can improve, creating a continuous learning atmosphere.
Encouraging Ownership and Accountability
Coaching leaders encourage their team members to take ownership of their tasks and outcomes. They build a culture of accountability by trusting their team and encouraging independence.
Celebrating Successes
Recognizing and celebrating successes, no matter how small, is essential in a coaching leadership style. This boosts morale and motivates the team to maintain high performance.
Benefits of a Coaching Leadership Style
This leadership style can lead to high engagement, increased job satisfaction, and improved performance as team members feel supported and invested in their growth. It’s particularly effective in environments where learning and development are valued, and innovation is key to success.
5.The Coercive Leader
A coercive leader is someone who relies on force, control, or pressure to lead a team. This style of leadership often involves a “do what I say” approach, emphasizing strict compliance and conformity. Coercive leaders typically use authority to command tasks and maintain order, often focusing on discipline, clear rules, and consequences for non-compliance.

Characteristics of a Coercive Leader
Top-Down Control: Coercive leaders centralize decision-making power, giving limited autonomy to their team members.
Rigid Rules and Policies: They tend to impose strict guidelines, ensuring that everyone follows protocols.
Short-Term Focus: Often prioritizing immediate results over long-term development, which can hinder innovation and morale.
Risk of Low Morale: The rigid structure and lack of flexibility can lead to decreased engagement and motivation among team members.
When Coercive Leadership Works
While coercive leadership is generally not favorable in environments where creativity and collaboration are essential, it can be effective in certain situations:
Crisis Management: In emergencies, this leadership style can provide the quick decisions needed for safety and control.
Turnarounds: When teams or organizations are underperforming, a coercive leader can bring in a structured approach to enforce necessary changes.
High-Stakes or High-Risk Environments: For teams that operate in critical situations, like military or certain public safety roles, clear commands can ensure safety and efficiency.
Downsides of Coercive Leadership
A coercive leader’s focus on compliance can suppress creativity, autonomy, and innovation. Over time, the lack of flexibility and empathy may result in:
Low Morale: Team members may feel undervalued and disengaged.
High Turnover: The high-pressure environment often leads to burnout and attrition.
Reduced Innovation: The rigid structure can stifle ideas and inhibit creative problem-solving.
Balancing Coercive Leadership
To be effective without damaging morale, leaders using a coercive approach might incorporate other styles:
Coaching: Integrating feedback and development alongside discipline.
Democratic Leadership: Allowing some degree of collaboration, especially once a crisis has been averted.
Affiliative Approach: Building a stronger emotional connection with the team, especially after a period of high pressure.
6.The Democratic Leader
In democratic leadership, the leader encourages open communication and active participation from team members in decision-making processes. This style values input from everyone involved and works to create a sense of equality and collaboration. Democratic leaders prioritize team feedback and consider everyone’s perspectives to shape decisions, ensuring that the group feels respected, valued, and motivated.

Here are some key characteristics of democratic leadership:
Collaboration and Participation: Decisions are made with input from team members, and the leader promotes discussions, listens actively, and integrates the team’s ideas.
Encouraging Creativity and Innovation: By inviting team members to share their ideas, democratic leaders foster a creative environment where unique solutions are more likely to emerge.
Building Trust and Respect: Team members feel trusted and respected because they have a voice in the decision-making process, which often leads to higher morale and a stronger commitment to the team’s goals.
Transparency: Democratic leaders are often open about the rationale behind decisions, helping team members understand the decision-making process and aligning them toward common objectives.
Shared Responsibility: In this style, responsibility for outcomes is shared, meaning successes are celebrated collectively, and challenges are tackled as a team.
https://www.linkedin.com/in/satish-kakri-17224417/
https://nimblefoundation.org/
https://nimblefoundation.org/our-clients.html
Thanks for reading.