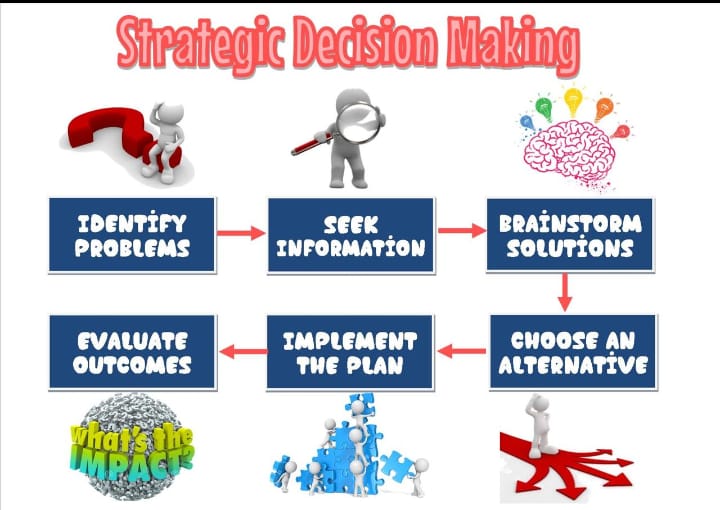
1) What is calmness?
Calmness is a state of mental and emotional tranquility. It involves being free from agitation, excitement, or disturbance. Calmness is characterized by a sense of peace, relaxation, and composure, even in stressful or challenging situations. It can be cultivated through various practices such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and other stress-reduction techniques. Achieving calmness often allows for clearer thinking, better decision-making, and improved overall well-being.

2) Why do people get restive?
People can become restive for various reasons, often linked to feelings of discomfort, dissatisfaction, or impatience. Some common reasons include:
Boredom or Lack of Stimulation: When people are bored or not sufficiently engaged, they may become restless and seek something to do.
Discomfort: Physical discomfort, such as being in a cramped space or an uncomfortable position, can make people fidgety and uneasy.
Anxiety or Stress: High levels of anxiety or stress can lead to restlessness. This can be due to worries about personal issues, work, or broader societal concerns.
Impatience: Waiting for something, especially if it takes longer than expected, can make people impatient and restless.

Unmet Needs or Desires: When people’s needs or desires are not being met, they can become agitated and restless.
Monotony or Routine: A lack of variety or change in daily routines can lead to restiveness as people seek novelty and excitement.
Environment: Certain environments can contribute to restlessness. For example, noisy or chaotic surroundings can make it difficult to relax.
Medical Conditions: Some medical conditions, such as ADHD, restless leg syndrome, or hyperthyroidism, can cause physical restlessness.
3) What are reasons behind anxiety?
Anxiety can be caused by a combination of factors, which can vary from person to person. Here are some common reasons behind anxiety:

Genetics: A family history of anxiety disorders can increase the likelihood of experiencing anxiety.
Brain Chemistry: Imbalances in brain chemicals like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine can affect mood and anxiety levels.
Personality: Certain personality traits, such as being highly sensitive, introverted, or perfectionistic, can make individuals more prone to anxiety.
Environmental Factors: Stressful life events, such as trauma, abuse, the death of a loved one, or significant life changes (e.g., moving, starting a new job), can trigger anxiety.
Medical Conditions: Chronic illnesses, thyroid disorders, heart disease, and other medical conditions can contribute to anxiety.
Substance Use: The use of caffeine, alcohol, and drugs can lead to or exacerbate anxiety symptoms. Withdrawal from these substances can also cause anxiety.
Brain Structure: Certain regions of the brain, particularly those involved in emotional regulation, may function differently in people with anxiety disorders.
Cognitive Patterns: Negative thought patterns, such as excessive worrying, catastrophizing, or overgeneralizing, can contribute to anxiety.
Behavioral Factors: Avoidance behaviors can perpetuate anxiety by preventing individuals from facing and overcoming their fears.
Social Factors: Social isolation, lack of support, and poor relationships can increase feelings of anxiety.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Poor diet and deficiencies in certain nutrients, such as magnesium and B vitamins, can affect mental health and contribute to anxiety.
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can influence anxiety levels.
4) How to deal with people who bully?
Dealing with bullies can be challenging, but there are several strategies that can help manage and potentially resolve the situation:

Stay Calm and Confident:
Bullies often seek a reaction. Staying calm and confident can sometimes defuse their attempts to provoke you.
Set Boundaries:
Clearly and firmly tell the bully to stop their behavior. Use assertive language and maintain eye contact if possible.
Avoid Isolation:
Spend time with friends or colleagues who can provide support. Bullies are less likely to target someone who is not alone.
Document Incidents:
Keep a record of what happened, including dates, times, and witnesses. This documentation can be useful if you need to report the bullying.
Seek Support:
Talk to friends, family members, or a trusted person about what’s happening. Emotional support can make a significant difference.
Report the Bullying:
If the bullying occurs at work or school, report it to the appropriate authorities, such as a supervisor, HR department, or school administration.
Practice Self-care:
Engage in activities that you enjoy and that help you relax. Taking care of your mental and physical health is important when dealing with stress.
Learn Conflict Resolution Skills:
Sometimes, understanding how to effectively communicate and resolve conflicts can help in dealing with bullies.
Avoid Retaliation:
Responding with aggression can escalate the situation. It’s often better to respond with calmness or remove yourself from the situation if possible.
Professional Help:
If the bullying is causing significant distress, consider seeking help from a counselor or therapist.
5) What role communication skills play in maintaining your calmness?
Communication skills play a crucial role in maintaining calmness in various ways. Here’s how:

Effective Expression: When you can articulate your thoughts and feelings clearly, it reduces misunderstandings and potential conflicts. This clarity often leads to a more peaceful interaction, helping you remain calm.
Active Listening: Good communication involves listening attentively. When you listen carefully to others, you gain a better understanding of their perspectives and concerns, which can prevent jumping to conclusions or reacting impulsively.
Conflict Resolution: Strong communication skills enable you to navigate conflicts constructively. You can express your feelings calmly, listen to the other party, and work towards a resolution without escalating tensions.
Stress Management: Being able to communicate effectively helps in expressing stress or frustration in a healthy manner. Whether it’s seeking support or explaining your needs, clear communication reduces the likelihood of bottling up emotions that could lead to outbursts.
Building Relationships: Calm and effective communication fosters trust and respect in relationships. It creates an environment where both parties feel heard and valued, promoting harmony and reducing the likelihood of misunderstandings.
Thanks for reading.