1) What is strategic decision process?
The strategic decision process refers to the systematic approach used by organizations to make long-term, significant decisions that shape the direction and scope of their activities. It involves several stages and key elements to ensure that decisions align with the organization’s goals, capabilities, and external environment. Here’s an overview of the strategic decision process:
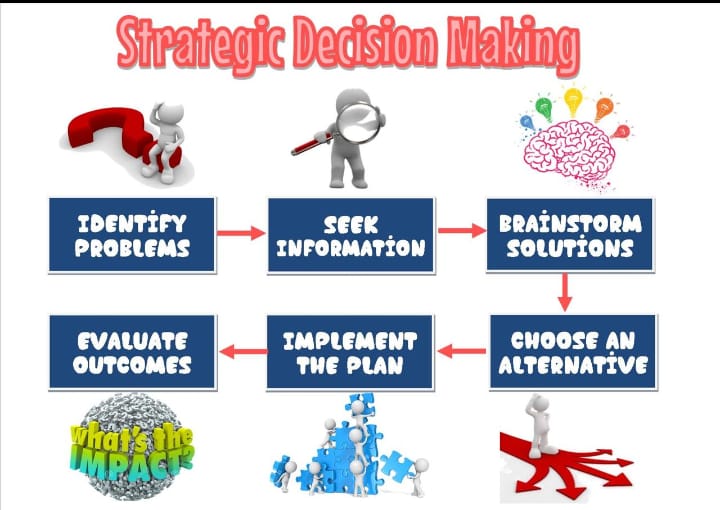
Problem Identification: Recognizing and clearly defining the problem or opportunity that requires a strategic decision. This involves understanding the context and scope of the issue.
Environmental Analysis: Gathering and analyzing information about the external environment, including market trends, competition, regulatory landscape, and economic conditions. Tools like PESTEL (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, Legal) analysis and SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis are often used.
Internal Analysis: Assessing the organization’s internal resources, capabilities, and core competencies. This includes evaluating financial resources, human resources, technology, and organizational culture.
Setting Objectives: Establishing clear, measurable, and achievable objectives that the decision aims to accomplish. These objectives should be aligned with the overall mission and vision of the organization.
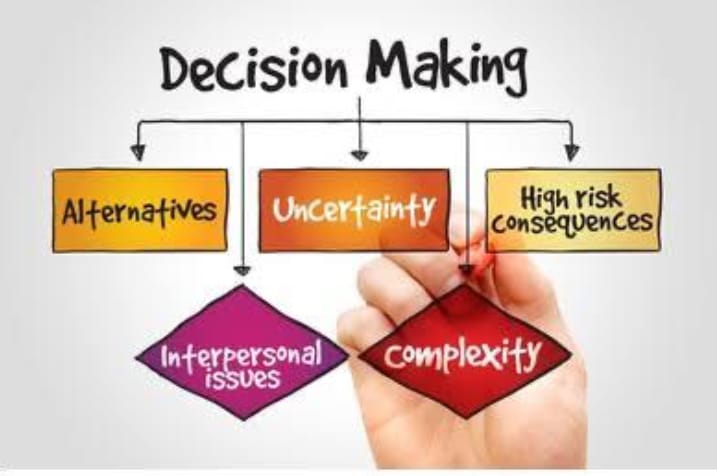
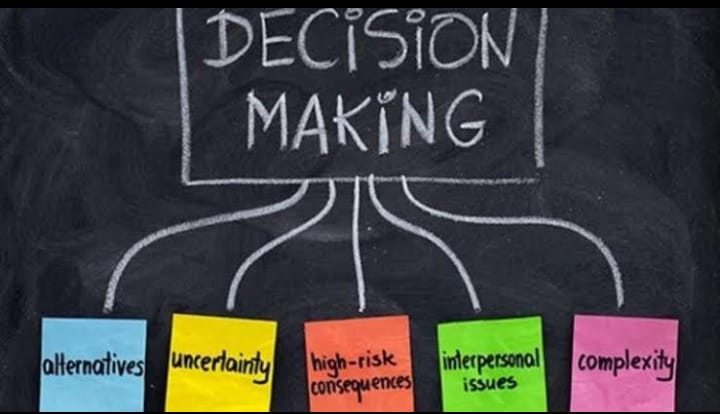
Generating Alternatives: Developing a range of potential strategies or courses of action that could address the problem or opportunity. Creativity and innovation are essential in this stage to ensure a wide array of options.
Evaluating Alternatives: Assessing the feasibility, risks, and potential impact of each alternative. This involves using quantitative and qualitative analysis methods, such as cost-benefit analysis, scenario planning, and decision trees.
Making the Decision: Choosing the best alternative based on the evaluation. This step often involves deliberation and consensus-building among key stakeholders and decision-makers.
Implementation: Developing a detailed action plan to execute the chosen strategy. This includes assigning responsibilities, allocating resources, setting timelines, and establishing monitoring mechanisms.
Monitoring and Control: Continuously tracking the implementation progress and measuring the outcomes against the set objectives. This step helps in identifying any deviations from the plan and making necessary adjustments.
Review and Feedback: Analyzing the overall effectiveness of the decision and the process used to make it. This includes learning from successes and failures to improve future decision-making processes.
2) How to be decisive?
Being decisive involves making decisions confidently and efficiently. Here are some strategies to help you become more decisive:
1. Gather Information
Research: Gather relevant information to understand the options and potential outcomes.
Consult Experts: Seek advice from knowledgeable people to get different perspectives.
2. Clarify Your Goals
Identify Objectives: Be clear about what you want to achieve.
Prioritize: Determine what is most important and align your decisions with these priorities.
3. Evaluate Options
List Pros and Cons: Write down the advantages and disadvantages of each option.
Consider Consequences: Think about the short-term and long-term impacts of each choice.
4. Trust Your Intuition
Gut Feeling: Sometimes your instinct can guide you when logical analysis is insufficient.
Past Experiences: Use lessons from previous decisions to inform your current choice.
5. Set a Deadline
Time Limit: Give yourself a reasonable timeframe to make the decision.
Avoid Overthinking: Excessive deliberation can lead to decision paralysis.
6. Reduce Choices
Limit Options: Too many choices can be overwhelming. Narrow down the options to the most viable ones.
Simplify: Focus on the most critical factors that will influence the decision.
7. Take Action
Commit: Once you’ve made a decision, commit to it and follow through.
Adjust if Necessary: Be flexible and willing to adjust your course if new information or circumstances arise.
8. Learn from Decisions
Reflect: After making a decision, reflect on the outcome to understand what worked and what didn’t.
Continuous Improvement: Use this reflection to improve your decision-making process for the future.
4) Why it is Necessary To stay positive in challenging situations?
Staying positive in challenging situations is crucial for several reasons, encompassing psychological, emotional, and practical benefits:
Resilience: A positive mindset enhances resilience, helping you bounce back from setbacks more quickly. It allows you to view challenges as opportunities for growth rather than insurmountable obstacles.
Mental Health: Maintaining a positive outlook reduces stress and anxiety, which can otherwise exacerbate the difficulty of the situation. It helps in preventing depression and other mental health issues.
Problem-Solving: Positivity fosters a more open and creative mindset, which is essential for effective problem-solving. When you are positive, you are more likely to think outside the box and find innovative solutions.
Motivation: A positive attitude keeps you motivated and focused on your goals. It helps in sustaining the energy and drive needed to overcome challenges.
Relationships: Positivity is contagious and can improve your interactions with others. In challenging times, strong relationships are crucial for support and collaboration, and a positive demeanor can help strengthen these bonds.
Health Benefits: Research has shown that positive thinking can improve physical health by boosting the immune system, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and promoting overall well-being.
Perception and Reality: The way you perceive a situation can influence its outcome. By staying positive, you are more likely to notice and seize opportunities that can lead to a better outcome.
Performance: Athletes, performers, and professionals often perform better under pressure when they maintain a positive attitude. This mindset helps in staying calm, focused, and confident, which can enhance performance.
Leadership: Positive leaders inspire and motivate their teams, even in difficult times. This can lead to better team cohesion, morale, and productivity.Self-fulfilling Prophecy: Positivity can create a self-fulfilling prophecy. If you believe that you can overcome a challenge, you are more likely to take the necessary actions to make it happen, thereby increasing your chances of success.
5) What are the best books available for learning about decision making?
Here are some of the best books for learning about decision making, covering various aspects such as cognitive psychology, behavioral economics, strategic thinking, and practical frameworks:
“Thinking, Fast and Slow” by Daniel Kahneman
This seminal book by Nobel laureate Daniel Kahneman explores the dual systems of thinking: System 1, which is fast, intuitive, and emotional; and System 2, which is slower, more deliberative, and logical. It provides deep insights into how decisions are made and the biases that influence them.
“Nudge: Improving Decisions About Health, Wealth, and Happiness” by Richard H. Thaler and Cass R. Sunstein
This book introduces the concept of “nudging” to improve decision-making in various aspects of life. Thaler and Sunstein provide practical examples of how subtle changes in the way choices are presented can significantly impact decisions.
“Predictably Irrational: The Hidden Forces That Shape Our Decisions” by Dan Ariely
Dan Ariely, a behavioral economist, delves into the irrational ways humans often behave and make decisions. The book explains why we make decisions that defy logic and how we can improve our decision-making processes.
“The Paradox of Choice: Why More Is Less” by Barry Schwartz
Barry Schwartz examines how having too many choices can lead to anxiety and decision paralysis. He discusses the psychological effects of choice overload and offers strategies to make better decisions by simplifying choices.
“Decisive: How to Make Better Choices in Life and Work” by Chip Heath and Dan Heath
The Heath brothers provide a framework called WRAP (Widen your options, Reality-test your assumptions, Attain distance before deciding, and Prepare to be wrong) to help improve decision-making in both personal and professional contexts.
“Thinking in Bets: Making Smarter Decisions When You Don’t Have All the Facts” by Annie Duke
Annie Duke, a professional poker player, shares insights into decision-making under uncertainty. The book emphasizes thinking in probabilities rather than absolutes and offers practical advice for making better decisions when the outcome is uncertain.
“Superforecasting: The Art and Science of Prediction” by Philip E. Tetlock and Dan M. Gardner
This book explores the skills and strategies used by superforecasters—individuals who are exceptionally good at predicting future events. It provides valuable lessons on improving forecasting accuracy and decision-making.