Public speaking is the act of delivering a structured and deliberate speech to an audience with the purpose of informing, persuading, entertaining, or inspiring them. It is a fundamental skill that has been practiced throughout human history, playing a critical role in politics, education, business, and various forms of advocacy. At its core, public speaking is about effective communication that connects the speaker with their audience, transcending the mere exchange of words to evoke emotion, understanding, and action.

The Evolution of Public Speaking
Public speaking dates back to ancient civilizations. In Ancient Greece and Rome, oratory was considered a vital skill for leaders, scholars, and politicians. Philosophers such as Aristotle and Cicero laid the foundation for modern rhetorical principles, emphasizing ethos (credibility), pathos (emotion), and logos (logic) as essential elements of persuasive speech. Over centuries, public speaking has evolved from formal speeches delivered in grand assemblies to modern settings, including classrooms, boardrooms, and virtual platforms.

Importance of Public Speaking
Public speaking is more than just standing in front of an audience and talking. It serves as a cornerstone for various personal and professional endeavors. Here are some reasons why public speaking is important:
Communication Skills: Effective public speaking improves overall communication skills, which are crucial for both personal relationships and professional success.
Influence and Persuasion: A skilled speaker can influence opinions, drive change, and persuade others, making it a powerful tool for leaders and advocates.
Building Confidence: Mastering public speaking boosts self-confidence, helping individuals overcome the fear of speaking in front of groups and assert themselves in other areas of life.
Education and Information Sharing: Public speaking is a primary method for educators, trainers, and thought leaders to disseminate knowledge and share ideas.
Networking and Career Advancement: In professional settings, being a good speaker can set you apart, opening doors to new opportunities and collaborations.
Engaging Audiences: A compelling speaker can entertain and inspire, creating memorable experiences for their audience.

Components of Public Speaking
Public speaking encompasses several key components that contribute to its effectiveness. These elements help a speaker connect with their audience and convey their message clearly.
1. Content
The foundation of any good speech is its content. This includes the main ideas, arguments, evidence, and examples that the speaker presents. Well-structured content ensures that the message is coherent and compelling.
Introduction: Grabs attention and sets the tone for the speech.
Body: Contains the main arguments, supported by evidence or stories.
Conclusion: Summarizes the key points and leaves a lasting impression.
2. Delivery
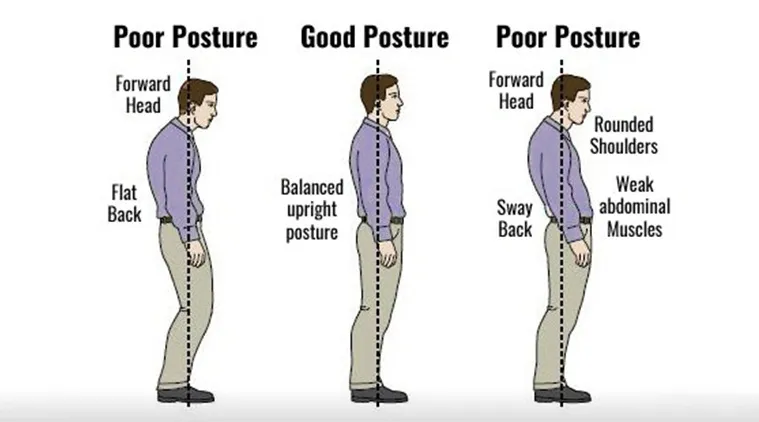
Delivery refers to how the speaker presents their content. This includes their tone of voice, body language, eye contact, and use of pauses. Effective delivery can captivate the audience and make the message more impactful.
Vocal Variety: Using different pitches, speeds, and volumes to emphasize key points.
Gestures and Posture: Enhancing the speech with expressive gestures and confident posture.
Eye Contact: Building rapport by engaging directly with the audience.
3. Audience Engagement
Understanding the audience is essential for successful public speaking. Tailoring the message to resonate with the audience’s interests, values, and expectations increases its impact.
Knowing Your Audience: Researching the demographics, preferences, and needs of your audience.
Interactive Elements: Encouraging questions, discussions, or feedback to foster engagement.
Cultural Sensitivity: Being aware of cultural nuances to avoid misunderstandings.
4. Visual Aids
Visual aids, such as slides, charts, videos, or props, can complement a speech by making complex information more digestible and visually appealing.
Simplicity: Keeping visuals clean and straightforward to avoid distractions.
Relevance: Ensuring that visuals enhance, rather than overshadow, the speech.
5. Preparation
Preparation is crucial for a successful public speaking performance. It involves researching the topic, organizing ideas, and rehearsing the delivery.
Practice: Rehearsing the speech multiple times to refine timing and delivery.
Feedback: Seeking constructive criticism to identify areas for improvement.
Contingency Planning: Preparing for potential challenges, such as technical issues or difficult questions.

Types of Public Speaking
Public speaking takes various forms, each with specific goals and contexts. Understanding these types helps speakers adapt their approach to suit different scenarios.
1. Informative Speaking
The goal of informative speaking is to educate the audience about a particular topic. Examples include lectures, seminars, and presentations in academic or professional settings.
2. Persuasive Speaking
Persuasive speaking aims to influence the audience’s beliefs, attitudes, or behaviors. This type is common in sales pitches, political speeches, and advocacy campaigns.
3. Entertaining Speaking
Entertaining speeches are designed to amuse and engage the audience. Comedians, storytellers, and event hosts often use this style to create enjoyable experiences.
4. Motivational Speaking
Motivational speakers inspire audiences to take action or adopt a positive mindset. They often use personal stories and powerful rhetoric to connect emotionally with their listeners.
5. Special Occasion Speaking
Special occasion speeches, such as toasts, eulogies, or award presentations, are tailored to specific events, balancing formality with personal touch.

Overcoming the Fear of Public Speaking
Glossophobia, or the fear of public speaking, is one of the most common phobias. Many people experience anxiety at the thought of speaking in front of an audience. However, this fear can be managed through practice and the right strategies.
1. Preparation
Thorough preparation helps reduce anxiety. Knowing your material inside and out builds confidence.
2. Practice
Rehearsing in front of friends, recording yourself, or practicing in front of a mirror helps you become comfortable with your speech.
3. Visualization
Imagining a successful performance can help boost confidence and reduce nervousness.
4. Breathing Techniques
Deep breathing exercises calm the nerves and help you focus.
5. Start Small
Begin by speaking to smaller groups or in informal settings before tackling larger audiences.

The Role of Technology in Public Speaking
Technology has transformed public speaking, offering new tools and platforms to enhance communication. Virtual presentations, webinars, and live streams allow speakers to reach global audiences.
Presentation Software: Tools like PowerPoint and Prezi help create professional slideshows.
Virtual Platforms: Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and similar platforms enable remote speaking opportunities.
Speech Analysis Tools: AI-powered applications provide feedback on delivery, tone, and pacing.
https://www.linkedin.com/in/satish-kakri-17224417/
https://nimblefoundation.org/
https://nimblefoundation.org/feedback.html
https://nimblefoundation.org/our-clients.html
Thanks for reading.